How the post pandemic era may exacerbate stress and anxiety disorders in individuals is a complicated question. Research suggests that prolonged social isolation caused by the COVID-19 pandemic may increase risk of stress and anxiety. In this article, we discuss the causes and symptoms of stress and anxiety in individuals during the pandemic and the effects of social isolation on mental health. We also discuss the role of social isolation in the development of anxiety and depression.
Symptoms Of Anxiety And Depression
As the number of newly diagnosed cases of COVID-19 increases, so too do symptoms of anxiety and depression. These symptoms may be related to other health conditions, such as substance abuse, or may be related to a mental health issue. In either case, mental health telemedicine services may be of assistance to those who experience these symptoms. Here is a list of the top articles published by Psychiatry Advisor in the year 2021.
Researchers assessed mental health symptoms among adults during the early phase of the COVID-19 pandemic, and looked for factors that predict them. In an online survey distributed via social media, 1,503 individuals answered questions about their mental health. In general, 22.3% of respondents had clinically significant levels of depressive symptoms, and 10.9% reported possible major depression. Similarly, 28.3% of respondents reported significant anxiety levels, with nine percent indicating severe anxiety. Findings were analyzed using multiple linear regression techniques, which revealed several common factors associated with both outcomes.
The study also investigated the impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on potentially disadvantaged populations. The researchers investigated the changes in depression and anxiety symptoms among individuals with prior mental disorders and their migration status. Overall, the findings suggest that the COVID-19 pandemic is likely to negatively affect people from underrepresented groups. This study also suggests that depression and anxiety symptoms may be more severe in groups with low socio-economic status and/or those with previous mental and sleep disorders.
Effect Of Social Isolation On Anxiety And Depression
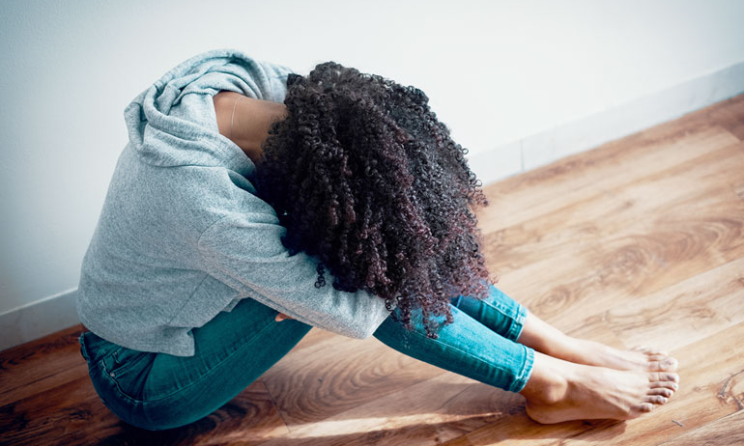
Public health situations can cause social isolation. Increased physical distance and fears of harm can contribute to loneliness and a negative self-concept. Moreover, studies have shown that social isolation is associated with a 26% increase in premature deaths. People who were socially isolated reported increased stress, anxiety attacks, emotional exhaustion, and insomnia. This increased loneliness may be related to COVID-19.
Consequently, the current containment measures are harmful to young people’s mental health. Children and young adults can experience high levels of loneliness as a result of school closures and social distancing. Studies indicate that one in three teenagers and half of 18-24 year-olds may experience high levels of loneliness during lockdowns. In addition, teenagers develop a sense of self by forming relationships with others outside their immediate family. In addition to affecting self-esteem and overall mental health, isolation may also exacerbate other pandemic-related problems.
Research pertaining to COVID-19 has indicated that it is likely to lead to increased levels of anxiety and depression among people exposed to the virus. While 90 per cent of countries have incorporated mental health into their COVID-19 response plans, major gaps remain. One of the biggest reasons for the increased incidence of depression and anxiety during the pandemic is the unprecedented stress that social isolation brings to people. Loneliness, financial worries, and family suffering are also identified as major causes of anxiety and depression. These symptoms may be linked to increased risk factors for suicide.
Effect Of Stress On Anxiety And Depression
A recent study found a link between reduced check-ins with current events and reduced anxiety. People who were more isolated from social interactions and who were more likely to be affected by the COVID-19 virus also experienced a higher rate of anxiety. Moreover, a recent study found that a lower check-in frequency was associated with a 19% lower risk of anxiety symptoms. The findings suggest that interventions targeting the negative effects of social isolation are necessary. These include strategies to address depression, sadness, loneliness, and post-traumatic stress.
A systematic review of the literature found that social isolation exacerbates the symptoms of depression and anxiety. Those who were in the epicenter of the pandemic experienced twice as many cases of severe depression than those who were not. Furthermore, sleep quality was significantly affected. Questions related to politics, religion, and the consumption of Chinese products were also associated with increased feelings of hopelessness and loneliness. Suicidal ideation was also found to be increased when the situation was worsened.
The results indicate that the presence of social isolation increases the risk of developing anxiety symptoms, and that this is associated with a societal burden. It is important to remember that this study represents the first approximation of a large theme and should be repeated with longer reference periods. The lack of certainty regarding the outcome of the COVID-19 outbreak is associated with stress, poor sleep, and physical complications.
Treatment For Stress and Anxiety Disorders?
Anxiety is a natural reaction to stress, an emotional and physical response that helps the body prepare for challenging situations. Although stress can be beneficial, constant, chronic exposure can have adverse effects. In addition to increasing stress, chronic stress also puts you at risk of physical and mental disorders. Fortunately, there are many natural treatments for anxiety. Some of these include proper rest and eating a balanced diet. But if you’re looking for an effective treatment for sleep disorders?, these are the best options.
Sleep Anxiety Disorders
If you are experiencing trouble sleeping due to your anxiety or stress, your doctor can prescribe medication to help you fall asleep fast at night. If you find that sleep aids don’t help you fall asleep, try another method. You can listen to relaxing music or read until you feel sleepy. If you can’t sleep, try meditation. Meditation helps to distract your mind from thoughts that are keeping you up at night. If you don’t find meditation to be helpful, talk with your doctor about other options.
Healthy Diet
A healthy diet can be a key component of effective anxiety management. Research has shown that a diet rich in vegetables and fruits can relieve symptoms of anxiety. Also, changing your diet may help you sleep better and wake up early in the morning. A diet that includes healthy fats and whole grains can support optimal brain functioning and improve your memory recall. You can incorporate more healthy fats and carbohydrates into your daily diet by increasing your intake of fruits and vegetables.
Conclusion Anxiety Disorders
However, early recognition is critical to speed recovery. While the signs of postnatal depression can vary, it is important to remember that they do not necessarily indicate postpartum depression. The symptoms of postnatal depression are the same as those of the “baby blues” but may be more severe.
Author Bio:
Larry Alton is a blogger and passionate writer at. He loves cooking and is fond of traveling.